Aphasia and Speech Therapy
Regaining Language After Brain Injury
Language is a cornerstone of human communication, and losing the ability to express thoughts and feelings can be devastating. Aphasia, a language disorder that often results from brain injury or damage, can disrupt the lives of those affected. However, there is hope for recovery through a specialized form of therapy: speech therapy. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of aphasia and explore how speech therapy plays a pivotal role in helping individuals regain their language skills after a brain injury.
Understanding Aphasia
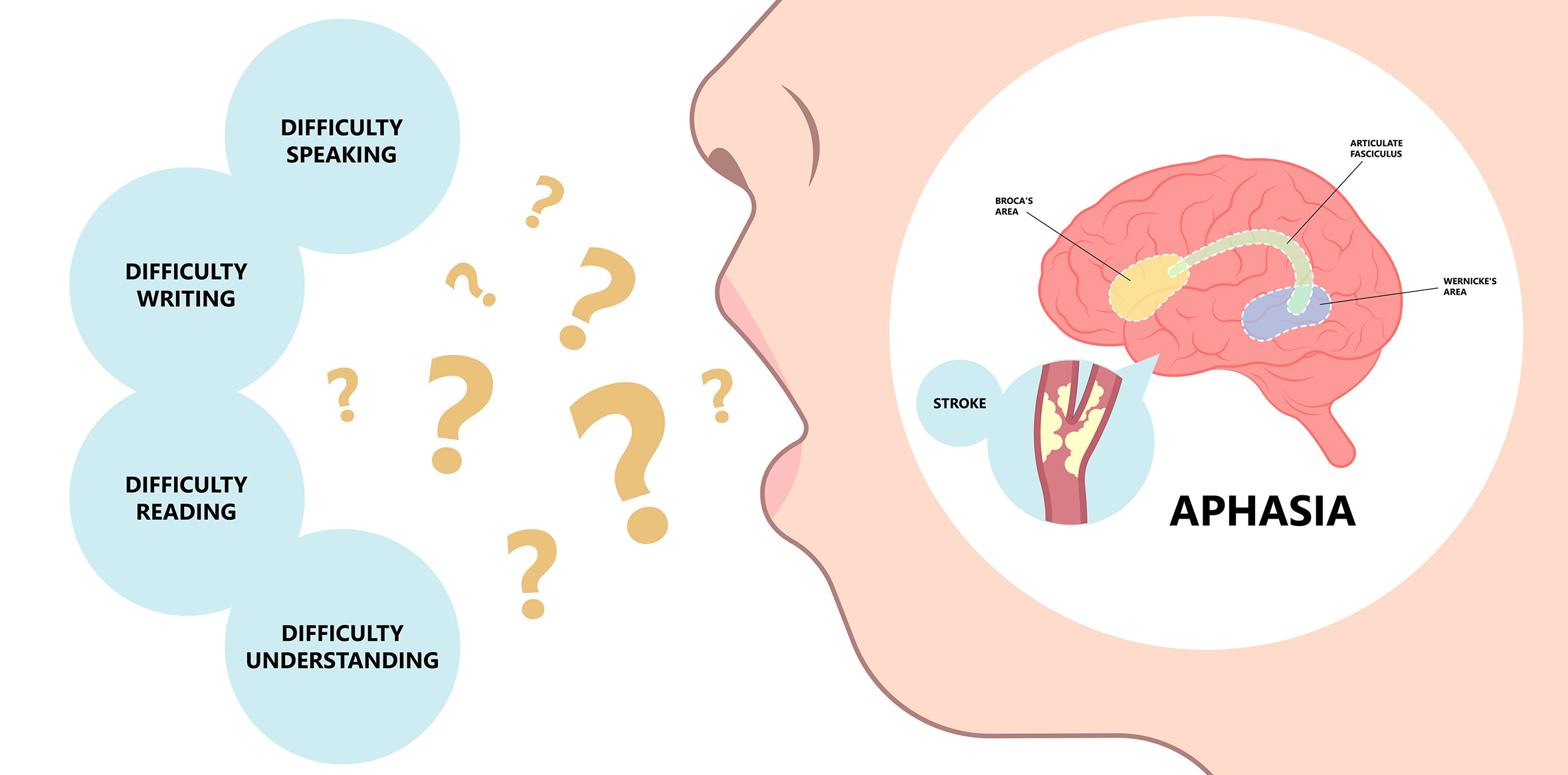
Aphasia is a neurological condition that impairs a person’s ability to understand, produce, or use language effectively. It most commonly occurs after brain injuries such as strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or other neurological conditions. Aphasia can manifest in various ways, affecting speaking, listening, reading, and writing skills to varying degrees. Each case is unique, as the specific type and severity of aphasia depends on the location and extent of brain damage.
Types of Aphasia
There are several different types of aphasia, including:
- Broca’s Aphasia: This type is characterized by difficulty in producing speech. Individuals with Broca’s aphasia may struggle to form grammatically correct sentences and experience frustration due to their inability to convey their thoughts effectively.
- Wernicke’s Aphasia: Wernicke’s aphasia primarily affects comprehension and the ability to choose the right words. Individuals with this type of aphasia may produce speech that is fluent but incomprehensible.
- Global Aphasia: Global aphasia is the most severe form, affecting all aspects of language, including speaking, understanding, reading, and writing. Individuals with global aphasia often have very limited communication abilities.
- Anomic Aphasia: In anomic aphasia, individuals have difficulty finding the right words to express their thoughts, making their speech hesitant and filled with pauses.
The Role of Speech Therapy in Aphasia Rehabilitation
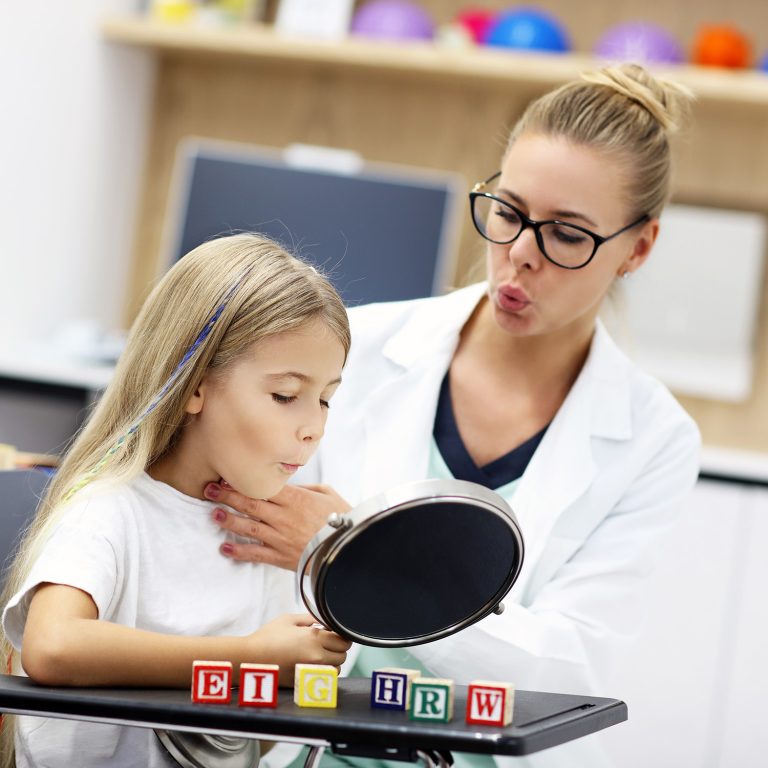
Speech therapy is the cornerstone of aphasia rehabilitation. It provides structured and evidence-based interventions aimed at helping individuals regain their language abilities and improve their overall quality of life. Here’s how speech therapy plays a pivotal role in aphasia recovery:
- Individualized Assessment: Speech therapy begins with a thorough assessment to understand the specific language deficits and needs of the person with aphasia. This evaluation forms the basis for creating a personalized treatment plan.
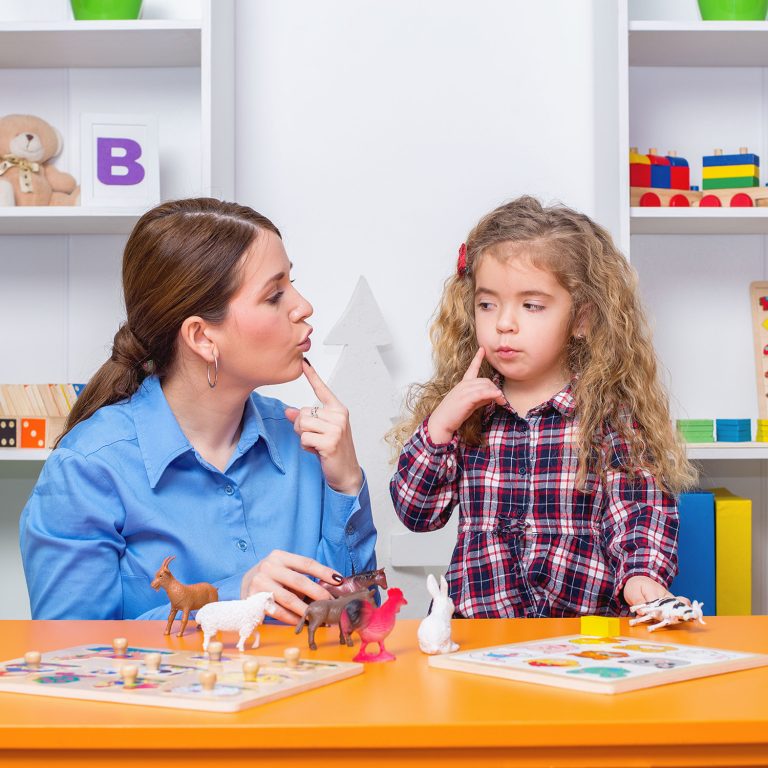
- Targeted Interventions: Speech therapists work with individuals to address the specific aspects of language affected by aphasia. These interventions often involve exercises to improve speech production, comprehension, reading, and writing skills.
- Oral and Written Language Exercises: Speech therapy includes a range of exercises and activities tailored to each person’s abilities and challenges. These exercises may involve repeating words and sentences, practicing sound patterns, and working on reading and writing skills.
- Communication Strategies: Speech therapists teach strategies to help individuals compensate for their language deficits. These may include using gestures, pictures, or communication boards to support effective communication.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention with speech therapy is crucial in aphasia recovery. The brain has an incredible ability to rewire and adapt after injury, a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity. By starting speech therapy as soon as possible, individuals with aphasia can capitalize on their brain’s ability to create new neural pathways, resulting in more significant and rapid language recovery.
Aphasia is a challenging condition that can drastically affect an individual’s ability to communicate effectively. However, with the dedicated guidance of speech therapy, there is hope for improvement and recovery. Speech therapists work diligently to help individuals with aphasia regain their language skills, providing them with the tools and strategies to communicate more effectively. If you or a loved one is facing aphasia after a brain injury, don’t underestimate the transformative power of speech therapy in reclaiming language and enhancing quality of life. It is a journey toward rebuilding communication and regaining a vital part of one’s identity.
Please Share
categories
Recent Posts

Aphasia and Speech Therapy
Regaining Language After Brain Injury
Language is a cornerstone of human communication, and losing the ability to express thoughts and feelings can be devastating. Aphasia, a language disorder that often results from brain injury or damage, can disrupt the lives of those affected. However, there is hope for recovery through a specialized form of therapy: speech therapy. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of aphasia and explore how speech therapy plays a pivotal role in helping individuals regain their language skills after a brain injury.
Understanding Aphasia
Aphasia is a neurological condition that impairs a person’s ability to understand, produce, or use language effectively. It most commonly occurs after brain injuries such as strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or other neurological conditions. Aphasia can manifest in various ways, affecting speaking, listening, reading, and writing skills to varying degrees. Each case is unique, as the specific type and severity of aphasia depends on the location and extent of brain damage.
Types of Aphasia
There are several different types of aphasia, including:
- Broca’s Aphasia: This type is characterized by difficulty in producing speech. Individuals with Broca’s aphasia may struggle to form grammatically correct sentences and experience frustration due to their inability to convey their thoughts effectively.
- Wernicke’s Aphasia: Wernicke’s aphasia primarily affects comprehension and the ability to choose the right words. Individuals with this type of aphasia may produce speech that is fluent but incomprehensible.
- Global Aphasia: Global aphasia is the most severe form, affecting all aspects of language, including speaking, understanding, reading, and writing. Individuals with global aphasia often have very limited communication abilities.
- Anomic Aphasia: In anomic aphasia, individuals have difficulty finding the right words to express their thoughts, making their speech hesitant and filled with pauses.
The Role of Speech Therapy in Aphasia Rehabilitation
Speech therapy is the cornerstone of aphasia rehabilitation. It provides structured and evidence-based interventions aimed at helping individuals regain their language abilities and improve their overall quality of life. Here’s how speech therapy plays a pivotal role in aphasia recovery:
- Individualized Assessment: Speech therapy begins with a thorough assessment to understand the specific language deficits and needs of the person with aphasia. This evaluation forms the basis for creating a personalized treatment plan.
- Targeted Interventions: Speech therapists work with individuals to address the specific aspects of language affected by aphasia. These interventions often involve exercises to improve speech production, comprehension, reading, and writing skills.
- Oral and Written Language Exercises: Speech therapy includes a range of exercises and activities tailored to each person’s abilities and challenges. These exercises may involve repeating words and sentences, practicing sound patterns, and working on reading and writing skills.
- Communication Strategies: Speech therapists teach strategies to help individuals compensate for their language deficits. These may include using gestures, pictures, or communication boards to support effective communication
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention with speech therapy is crucial in aphasia recovery. The brain has an incredible ability to rewire and adapt after injury, a phenomenon known as neuroplasticity. By starting speech therapy as soon as possible, individuals with aphasia can capitalize on their brain’s ability to create new neural pathways, resulting in more significant and rapid language recovery.
Aphasia is a challenging condition that can drastically affect an individual’s ability to communicate effectively. However, with the dedicated guidance of speech therapy, there is hope for improvement and recovery. Speech therapists work diligently to help individuals with aphasia regain their language skills, providing them with the tools and strategies to communicate more effectively. If you or a loved one is facing aphasia after a brain injury, don’t underestimate the transformative power of speech therapy in reclaiming language and enhancing quality of life. It is a journey toward rebuilding communication and regaining a vital part of one’s identity.
Please Share
You May Also Like