Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery
How Occupational Therapy Supports Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery: A New Perspective
Have you ever wondered how one split-second moment can turn your life upside down? Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an unexpected, life-altering event that can strike anyone at any time, and can place an unexpected impact on that person’s life. Fortunately, there’s hope in the form of occupational therapy. In this article, we will explore how occupational therapy plays a crucial role in supporting traumatic brain injury recovery and provides a fresh perspective on rehabilitation.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery and The Role of Occupational Therapy
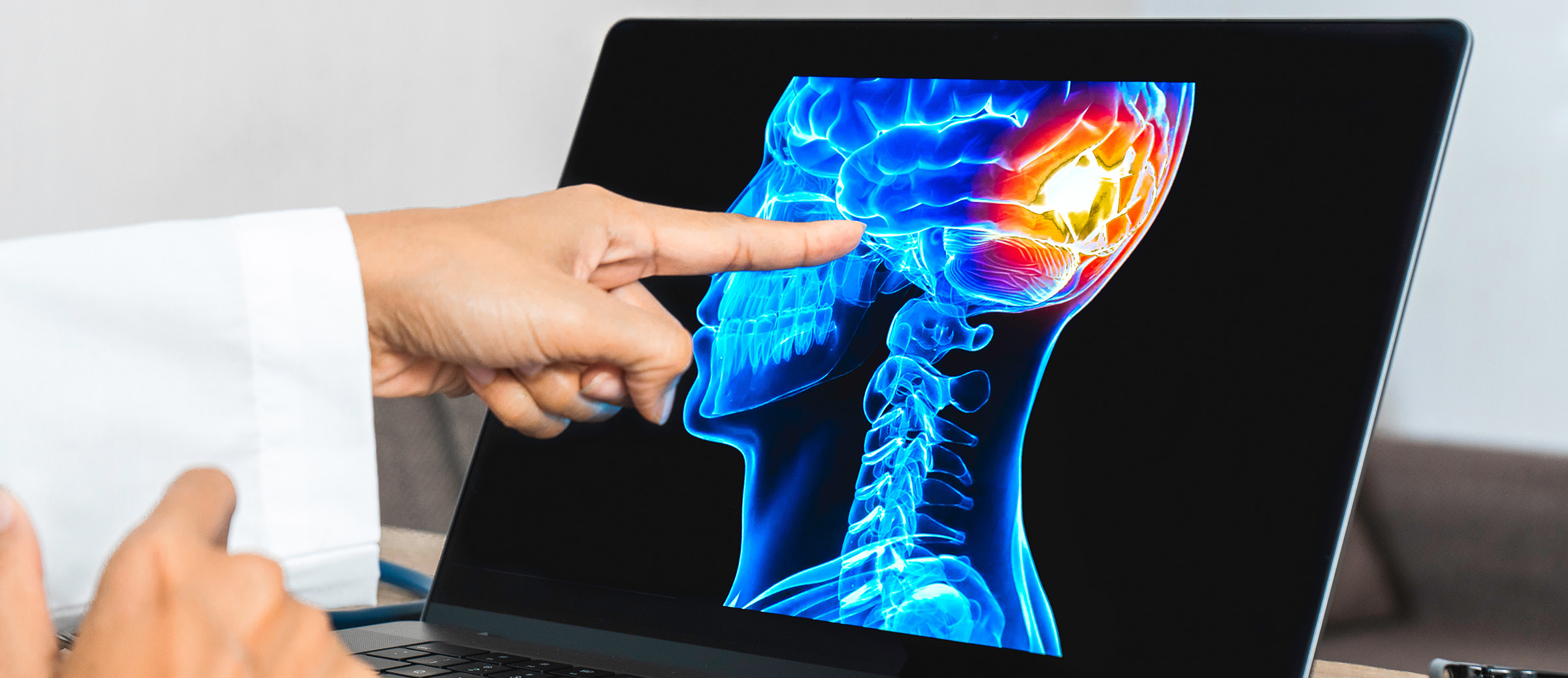
TBI is an injury that occurs when there is a sudden, severe blow to the head or when an object penetrates the skull. It can result from a wide range of events, such as car accidents, falls, sports injuries, or military combat. The consequences of a TBI can be physical, cognitive, emotional, and even affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities.
Occupational therapy, often abbreviated as OT, is a rehabilitative approach that focuses on helping individuals regain the skills and independence they need to perform everyday activities. Occupational therapy can be a game-changer for traumatic brain injury recovery and here’s how:
Regaining Independence:
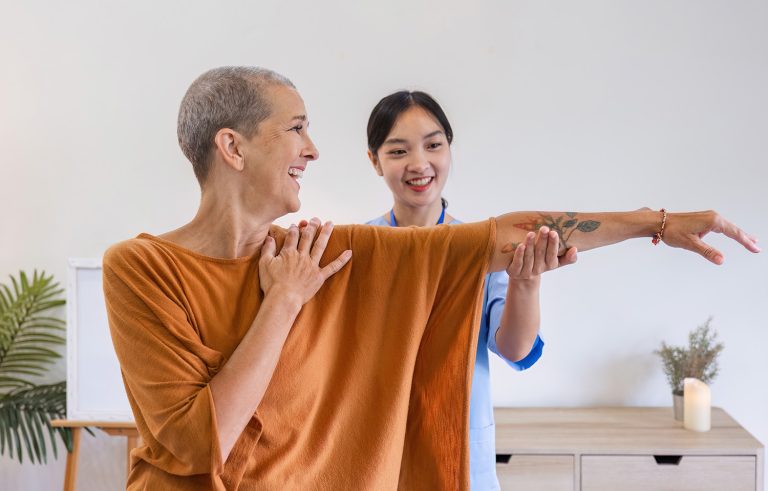
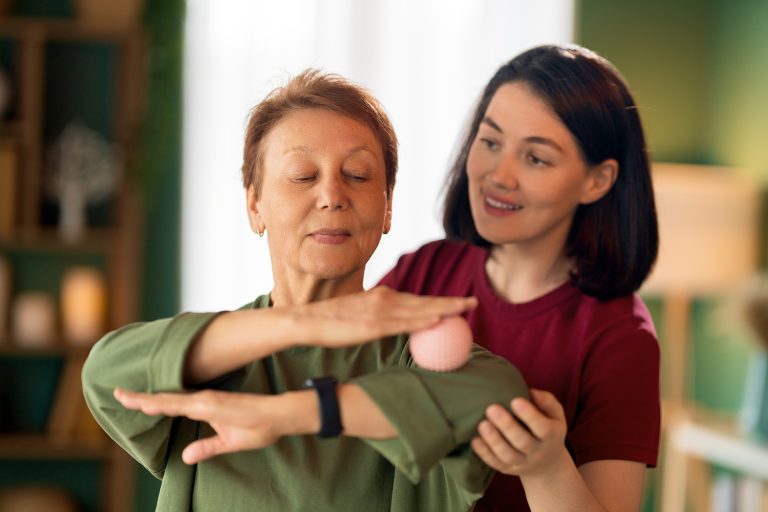
One of the primary goals of occupational therapy in traumatic brain injury recovery is to help individuals regain their independence. TBI can result in physical limitations, such as impaired motor skills, balance, and coordination. Occupational therapists work closely with patients to assess these limitations and develop customized rehabilitation plans to address them. Through targeted exercises and strategies, occupational therapy helps individuals regain the physical abilities they need to perform daily tasks.
Cognitive Rehabilitation:
TBI often leads to cognitive challenges, such as memory problems, difficulties with attention and concentration, and impaired problem-solving skills. Occupational therapists are trained to provide cognitive rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury recovery, which involves exercises and strategies to help individuals regain their cognitive function. These techniques can be critical for TBI survivors as they strive to resume their daily activities, return to work, and maintain their independence.
New Techniques and Assistive Devices:
Occupational therapy also introduces new techniques and assistive devices to help TBI survivors overcome physical limitations. These may include tools for daily living like modified utensils, dressing aids, and mobility devices. The usage of assistive devices can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to engage in essential activities and regain a sense of normalcy.
Community Reintegration:
Occupational therapy goes beyond the clinical setting to help traumatic brain injury survivors reintegrate into their communities. Occupational therapists work with patients to set and achieve goals related to returning to work, engaging in social activities, and pursuing hobbies. This community-based approach is essential for restoring a sense of purpose and social connection, which can significantly aid in the recovery process.
Vocational/Workplace Rehabilitation:
For TBI survivors who were employed prior to their injury, occupational therapy plays a vital role in vocational rehabilitation. Occupational therapists help assess the individual’s job-related skills, recommend accommodations, and develop strategies to ensure a smooth transition back into the workplace. Vocational rehabilitation through occupational therapy not only enhances self-esteem but also improves financial stability for survivors.
Long-Term Support:
The recovery process after a TBI is not always linear. Patients may encounter new challenges or setbacks as they continue their journey. Occupational therapy offers long-term support, making necessary adjustments to rehabilitation plans and ensuring individuals can maintain and improve their quality of life over time.
Conclusion:
Traumatic brain injury can be a life-changing event, but occupational therapy offers a new perspective on traumatic brain injury recovery. From addressing physical and cognitive challenges to recommending adaptive techniques and assistive devices, occupational therapists play a vital role in supporting TBI survivors. Whether it’s regaining independence, reintegrating into the community, or pursuing vocational rehabilitation, occupational therapy provides the tools and support needed to navigate the complex challenges of TBI recovery.
If you or someone you know is recovering from a traumatic brain injury, consider seeking the expertise of an Occupational Therapist. With determination and support from occupational therapy, the path to recovery becomes a journey toward renewed independence and a bright future.
Please Share
categories
Recent Posts

Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery
How Occupational Therapy Supports Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery: A New Perspective
Have you ever wondered how one split-second moment can turn your life upside down? Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is an unexpected, life-altering event that can strike anyone at any time, and can place an unexpected impact on that person’s life. Fortunately, there’s hope in the form of occupational therapy. In this article, we will explore how occupational therapy plays a crucial role in supporting traumatic brain injury recovery and provides a fresh perspective on rehabilitation.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury Recovery and The Role of Occupational Therapy
TBI is an injury that occurs when there is a sudden, severe blow to the head or when an object penetrates the skull. It can result from a wide range of events, such as car accidents, falls, sports injuries, or military combat. The consequences of a TBI can be physical, cognitive, emotional, and even affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities.
Occupational therapy, often abbreviated as OT, is a rehabilitative approach that focuses on helping individuals regain the skills and independence they need to perform everyday activities. Occupational therapy can be a game-changer for traumatic brain injury recovery and here’s how:
Regaining Independence:
One of the primary goals of occupational therapy in traumatic brain injury recovery is to help individuals regain their independence. TBI can result in physical limitations, such as impaired motor skills, balance, and coordination. Occupational therapists work closely with patients to assess these limitations and develop customized rehabilitation plans to address them. Through targeted exercises and strategies, occupational therapy helps individuals regain the physical abilities they need to perform daily tasks.
Cognitive Rehabilitation:
TBI often leads to cognitive challenges, such as memory problems, difficulties with attention and concentration, and impaired problem-solving skills. Occupational therapists are trained to provide cognitive rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury recovery, which involves exercises and strategies to help individuals regain their cognitive function. These techniques can be critical for TBI survivors as they strive to resume their daily activities, return to work, and maintain their independence.
New Techniques and Assistive Devices:
Occupational therapy also introduces new techniques and assistive devices to help TBI survivors overcome physical limitations. These may include tools for daily living like modified utensils, dressing aids, and mobility devices. The usage of assistive devices can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to engage in essential activities and regain a sense of normalcy.
Community Reintegration:
Occupational therapy goes beyond the clinical setting to help traumatic brain injury survivors reintegrate into their communities. Occupational therapists work with patients to set and achieve goals related to returning to work, engaging in social activities, and pursuing hobbies. This community-based approach is essential for restoring a sense of purpose and social connection, which can significantly aid in the recovery process.
Vocational/Workplace Rehabilitation:
For TBI survivors who were employed prior to their injury, occupational therapy plays a vital role in vocational rehabilitation. Occupational therapists help assess the individual’s job-related skills, recommend accommodations, and develop strategies to ensure a smooth transition back into the workplace. Vocational rehabilitation through occupational therapy not only enhances self-esteem but also improves financial stability for survivors.
Long-Term Support:
The recovery process after a TBI is not always linear. Patients may encounter new challenges or setbacks as they continue their journey. Occupational therapy offers long-term support, making necessary adjustments to rehabilitation plans and ensuring individuals can maintain and improve their quality of life over time.
Conclusion:
Traumatic brain injury can be a life-changing event, but occupational therapy offers a new perspective on traumatic brain injury recovery. From addressing physical and cognitive challenges to recommending adaptive techniques and assistive devices, occupational therapists play a vital role in supporting TBI survivors. Whether it’s regaining independence, reintegrating into the community, or pursuing vocational rehabilitation, occupational therapy provides the tools and support needed to navigate the complex challenges of TBI recovery.
If you or someone you know is recovering from a traumatic brain injury, consider seeking the expertise of an Occupational Therapist. With determination and support from occupational therapy, the path to recovery becomes a journey toward renewed independence and a bright future.
Please Share