
National Diabetes Awareness Month
November is National Diabetes Awareness Month, and it is important for everyone to be aware of the signs and symptoms, how to treat, how to prevent pre-diabetes and Diabetes.
In the United States there are a total of 37.3 million people who have been diagnosed with diabetes (11.3% of the US population). There is a total of 96 million people aged 18 years or older that have a diagnosis of Pre-Diabetes (38.0% of the adult US population).
3 Types of Diabetes – Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and Gestational Diabetes.
Before people develop type 2 diabetes, they almost always have prediabetes—blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
● Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin every day to survive.
● Type 2 diabetes is when your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes.
● Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women who have never had diabetes. It increases your risk for type 2 diabetes later in life. Your baby is more likely to have obesity as a child or teen and develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
● Urinating often
● Feeling very thirsty
● Feeling very hungry – even though you are eating
● Extreme fatigue (tired)
● Blurry Vision
● Cuts/Bruises that are slow to heal
● Weight loss – even though you are eating more (Type 1 Diabetes)
● Tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands/feet (Type 2 Diabetes)
Tests to Determine if you have Pre-Diabetes or Diabetes
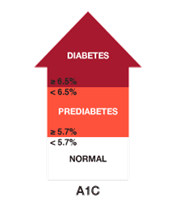
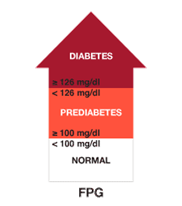
A1C test measures your average blood glucose for the past two to three months.
FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose) -This test checks your fasting blood glucose levels. Fasting means after not having anything to eat or drink (except water) for at least 8 hours before the test.
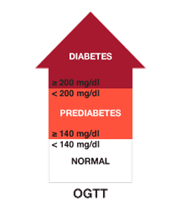
OGTT – The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood glucose levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink.
Ways to Prevent Pre-Diabetes & Diabetes
● Losing weight – even losing 5-10% of your current body weight will help to decrease your risk
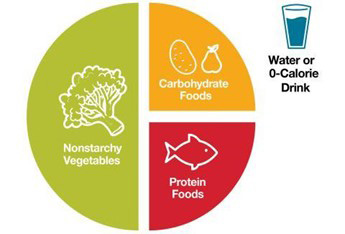
● Eating Healthy Food – eating a variety of foods; Trying not to eat too much food; Try not to eat too much of one type of food – especially carbohydrates; Space your meals evenly throughout the day; Avoid skipping meals
● Being active – slowly increase exercise to 30+ minutes each day
● Stress – needs to be kept under control

Please Share
categories
Recent Posts

National Diabetes Awareness Month
November is National Diabetes Awareness Month, and it is important for everyone to be aware of the signs and symptoms, how to treat, how to prevent pre-diabetes and Diabetes.
In the United States there are a total of 37.3 million people who have been diagnosed with diabetes (11.3% of the US population). There is a total of 96 million people aged 18 years or older that have a diagnosis of Pre-Diabetes (38.0% of the adult US population).
3 Types of Diabetes – Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and Gestational Diabetes.
Before people develop type 2 diabetes, they almost always have prediabetes—blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
● Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. If you have type 1 diabetes, you’ll need to take insulin every day to survive.
● Type 2 diabetes is when your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes.
● Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women who have never had diabetes. It increases your risk for type 2 diabetes later in life. Your baby is more likely to have obesity as a child or teen and develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
● Urinating often
● Feeling very thirsty
● Feeling very hungry – even though you are eating
● Extreme fatigue (tired)
● Blurry Vision
● Cuts/Bruises that are slow to heal
● Weight loss – even though you are eating more (Type 1 Diabetes)
● Tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands/feet (Type 2 Diabetes)
Tests to Determine if you have Pre-Diabetes or Diabetes



A1C test measures your average blood glucose for the past two to three months.
FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose) -This test checks your fasting blood glucose levels. Fasting means after not having anything to eat or drink (except water) for at least 8 hours before the test.
OGTT – The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood glucose levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink.
Ways to Prevent Pre-Diabetes & Diabetes
● Losing weight – even losing 5-10% of your current body weight will help to decrease your risk
● Eating Healthy Food – eating a variety of foods; Trying not to eat too much food; Try not to eat too much of one type of food – especially carbohydrates; Space your meals evenly throughout the day; Avoid skipping meals
● Being active – slowly increase exercise to 30+ minutes each day
● Stress – needs to be kept under control


Please Share